Introduction
Are you a dog owner eagerly anticipating the arrival of your fur baby's puppies? Or perhaps you're curious about the duration of a dog's pregnancy? Understanding the pregnancy length for dogs is crucial for preparing and caring for both the mother and her soon-to-be-born litter. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of dog pregnancies, providing you with valuable insights and practical advice.
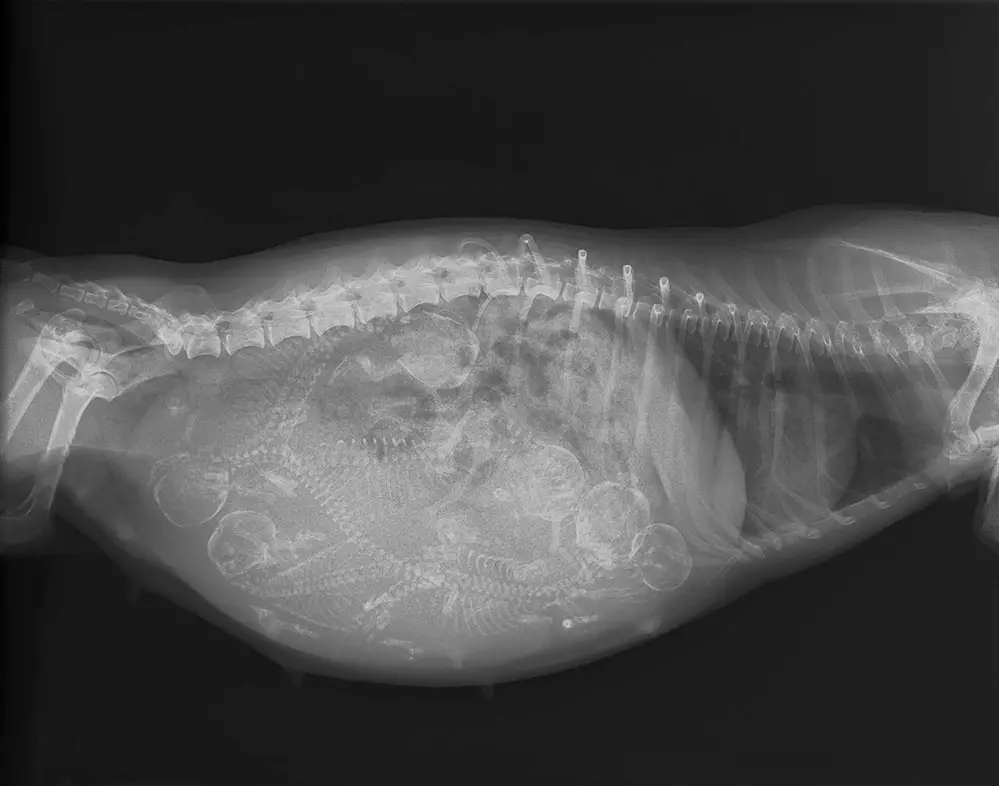
Source bowwowinsurance.com.au
Gestation Period: The Phases of Pregnancy
The gestation period for dogs typically ranges from 58 to 68 days, with an average of 63 days. This period, which encompasses the time from conception to birth, consists of three distinct phases:
Pre-Implantation (0-12 days)
During this phase, the fertilized eggs travel through the fallopian tubes towards the uterus. They implant into the uterine lining, marking the beginning of embryonic development.
Embryonic Development (13-30 days)
The embryos undergo rapid growth and differentiation during this period. The heart, brain, and other vital organs begin to form. The embryos are surrounded by a protective fluid-filled sac called the amnion.
Fetal Development (31 days to birth)
The fetuses take on their recognizable canine form during this phase. They grow rapidly, develop fur, and their bones and muscles continue to mature. The time of birth approaches, and the mother's body prepares for labor.
Factors Influencing Pregnancy Length
While the average gestation period for dogs is 63 days, several factors can influence the length, including:
Breed
Certain breeds, such as Giant breeds, tend to have longer pregnancies than smaller breeds. This is attributed to their larger size and the time required for their puppies to develop.
Number of Puppies
The number of puppies carried by the mother can also impact pregnancy length. Litters with a smaller number of puppies (1-3) typically have a shorter gestation period compared to litters with a larger number of puppies (more than 8).
Age of the Mother
Older mothers may have shorter pregnancies due to decreased uterine elasticity. First-time mothers, on the other hand, may have slightly longer pregnancies as their bodies adjust to the demands of carrying a litter.
Signs of Pregnancy in Dogs
Recognizing the signs of pregnancy in your dog is important for monitoring her well-being and preparing for the arrival of puppies. Some common indicators include:
Behavioral Changes
Pregnant dogs may exhibit changes in behavior, such as increased clinginess, decreased activity levels, or nesting behavior.
Physical Changes
Physical changes may include enlargement of the abdomen, swelling of the mammary glands, and a mucoid discharge from the vulva.
Increased Appetite
Pregnant dogs may experience an increase in appetite as their nutritional needs increase to support both themselves and the developing puppies.
Caring for a Pregnant Dog
Ensuring the well-being of a pregnant dog is paramount. Here are some tips for providing optimal care:
Nutrition
Provide a high-quality diet that meets the increased nutritional demands of pregnancy. Consult with your veterinarian to determine appropriate portion sizes and calorie intake.
Exercise
Moderate exercise is beneficial for pregnant dogs, but avoid strenuous activities that could put stress on the abdomen.
Veterinary Care
Regular veterinary checkups are crucial throughout pregnancy to monitor the mother's health and the puppies' development. Prenatal ultrasounds or X-rays may be recommended to determine the number of puppies and their well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding the pregnancy length for dogs is essential for dog owners and breeders alike. By being aware of the duration, phases, and factors influencing pregnancy, you can provide optimal care for your pregnant dog and eagerly anticipate the joyous arrival of her litter. For more informative articles on pet care, breeding, and animal health, be sure to check out our website.
FAQ about Dog Pregnancy Length
Q: How long is a dog pregnant?
- A: The average pregnancy length for dogs is 63 days (9 weeks) from the day of conception.
Q: When does a dog start showing signs of pregnancy?
- A: Visible signs of pregnancy, such as an enlarged abdomen and swollen nipples, usually appear around 4-5 weeks of pregnancy.
Q: How can I tell when my dog is pregnant?
- A: Apart from physical signs, a veterinarian can confirm pregnancy through an ultrasound or blood test.
Q: How does the size of the dog affect pregnancy length?
- A: Larger breeds may have slightly longer pregnancies than smaller breeds.
Q: Can the pregnancy length vary within the same breed?
- A: Yes, individual pregnancies can vary by a few days within the same breed.
Q: What is the safe period for my dog to get pregnant?
- A: The optimal time for breeding is usually between the 10th and 14th day of the estrus cycle.
Q: How many puppies can a dog have?
- A: The number of puppies can vary depending on the breed, size, and individual dog. The average litter size is 4-8 puppies.
Q: What should I do if my dog's pregnancy is longer than expected?
- A: If your dog's pregnancy exceeds 68 days, consult with your veterinarian to rule out any complications. Prolonged pregnancy can be a risk to both the mother and puppies.
Q: What are the signs of impending labor?
- A: Signs include restlessness, nesting, panting, and fluid discharge. Labor usually begins 24-48 hours after these symptoms appear.
Q: Do all dogs experience false pregnancies?
- A: No, not all dogs experience false pregnancies. If your dog shows signs of pregnancy without being bred, consult with your veterinarian to determine the cause.